In the world of physics and mathematics, the concepts of period and frequency play a crucial role in understanding the behavior of waves and oscillations. These terms are often used interchangeably, but they represent distinct aspects of periodic phenomena. The period refers to the time it takes for one complete cycle of a wave or oscillation to occur, while frequency indicates how many cycles occur in a unit of time. Grasping these concepts is essential for students, educators, and professionals in various fields, as they form the foundation of many scientific principles.
As we delve deeper into the relationship between period and frequency, it becomes clear that these concepts are not only relevant in physics but also have real-world applications in engineering, telecommunications, and even music. For instance, understanding the frequency of sound waves can help musicians tune their instruments, while in engineering, it can be crucial for designing systems that rely on oscillatory motion.
This article will explore the intricacies of period and frequency, addressing common questions, applications, and their significance across different domains. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of these terms and be able to apply this knowledge in practical situations.
What is the Definition of Period and Frequency?
The period is defined as the duration of time it takes for one complete cycle of a periodic event to occur. It is commonly measured in seconds. For instance, if a pendulum swings back and forth and takes 2 seconds to return to its starting position, its period is 2 seconds.
On the other hand, frequency is defined as the number of cycles that occur in a unit of time, typically measured in Hertz (Hz). One Hertz is equivalent to one cycle per second. Therefore, if the same pendulum completes 5 cycles in 10 seconds, its frequency would be 0.5 Hz (5 cycles/10 seconds).
How Are Period and Frequency Related?
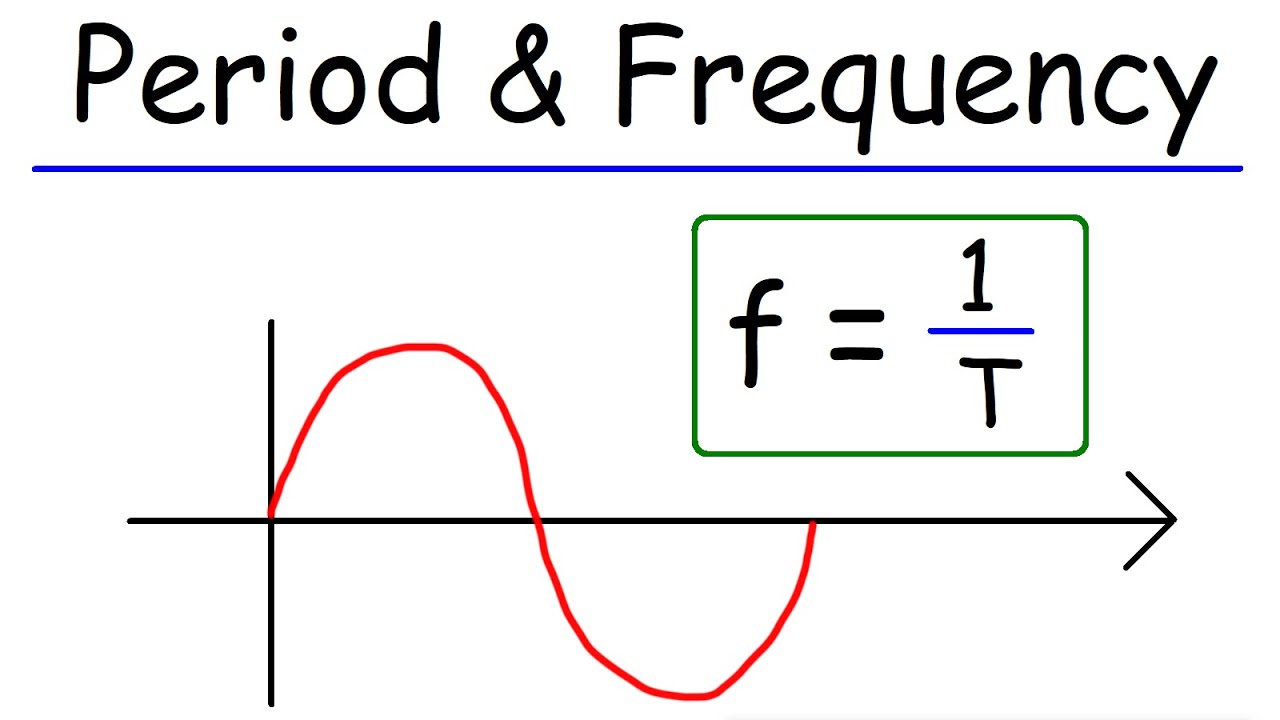
The relationship between period and frequency is straightforward and can be expressed mathematically. The formula connecting the two is:
Frequency (f) = 1 / Period (T)
This means that as the period increases, the frequency decreases, and vice versa. Understanding this inverse relationship is fundamental when analyzing various systems, from mechanical oscillators to electronic circuits.
What Are the Units of Measurement for Period and Frequency?
- Period: Measured in seconds (s)
- Frequency: Measured in Hertz (Hz), where 1 Hz = 1 cycle/second
Where Are Period and Frequency Used in Real Life?
Period and frequency can be observed in numerous applications, including:
- Sound: Musical notes have specific frequencies, which determine their pitch.
- Electronics: Oscillators generate signals at specific frequencies for communication technologies.
- Mechanics: The motion of springs and pendulums is analyzed using period and frequency.
- Biology: Biological rhythms, like heartbeats, can be studied through these concepts.
What Role Does Frequency Play in Music?
In the realm of music, frequency is vital for determining the pitch of notes. Musicians rely on specific frequencies to tune their instruments accurately. For example, the note A4 is typically tuned to 440 Hz, which serves as a standard reference pitch in Western music. Understanding the frequency of different notes allows musicians to create harmonious compositions and performances.
How Does Period and Frequency Impact Technology?
In technology, period and frequency are crucial in the design of circuits and communication systems. For instance, radio waves operate at specific frequencies, allowing for the transmission of information over long distances. Engineers must consider these properties when designing antennas and other communication devices to ensure they function effectively within the desired frequency range.
Can Period and Frequency Be Measured Accurately?
Yes, period and frequency can be measured accurately using various instruments. Common methods include:
- Oscilloscopes: These devices visually represent waveforms, allowing for accurate measurement of period and frequency.
- Frequency Counters: These instruments count the number of cycles occurring within a specific time frame.
Additionally, advancements in technology have led to the development of software applications that can analyze audio signals and provide precise measurements of period and frequency, further enhancing our ability to study these concepts.
What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Period and Frequency?
Many people often confuse period and frequency due to their close relationship. A common misconception is that a higher frequency implies a longer period, when in reality, they are inversely related. Understanding this distinction is crucial for anyone studying waves, oscillations, or any related fields.
How Can Knowledge of Period and Frequency Benefit You?
Grasping the concepts of period and frequency can provide numerous benefits, such as:
- Improving understanding of music theory and sound production.
- Enhancing skills in engineering and electronics.
- Facilitating a deeper comprehension of natural phenomena, such as earthquakes and waves.
In conclusion, the concepts of period and frequency are integral to various fields, from music to engineering. By understanding these terms and their applications, individuals can gain valuable insights that extend beyond the classroom and into real-world situations. Whether you are a student, a professional, or simply an enthusiast, mastering the relationship between period and frequency opens a world of possibilities.
You Might Also Like
Is WhatsApp Down? Understanding The Global Connectivity CrisisEmbracing The Art Of Basic Henna Designs
Exploring Preferences: Do You Like?
Unlocking The Secrets To An Effective Hair Care Routine
Exploring The Enigmatic Character Of Coraline's Other Father
Article Recommendations
- Elijah Hewson Height
- Jude Bellingham Parents Nationality
- Jessica Springsteen Married
- Michael Boulos Religious Beliefs
- Is Baron Trump Autistic
- Andy Bassich
- Robin Wright
- Super Bowl Wins For Eli Manning
- Sarah Jakes Roberts Age
- Kilmer Top Gun

![How to find the amplitude period and frequency of a trigonometric function?[Solved]](https://i2.wp.com/d138zd1ktt9iqe.cloudfront.net/media/seo_landing_files/ow-to-find-the-amplitude-period-and-frequency-of-a-trigonometric-functi-01-1620209825.png)